Plate heat exchangers: types, device and principle of operation
INTRODUCTION
A custom micro-fluid channel plate is one of the types of recuperative heat exchangers. Similarly, it comes on heat exchange between two media through a contact plate without mixing.
THE CONTENT OF THE ARTICLE
- Introduction
- Types, device and principle of operation of plate heat exchangers
- Gasketed plate heat exchangers
- Brazed heat exchangers
- Semi-welded heat exchangers
- Welded heat exchangers
- Application of plate heat exchangers
- Similarly, Plate Heat Exchanger Specifications
- Pros and cons of plate heat exchangers
- Advantages
- Flaws
- Conclusion
TYPES, DEVICE AND PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION OF PLATE HEAT EXCHANGERS
Basically, the principle of operation of all plate heat exchangers is the same:
- Heat carriers are supplied to the TO inputs.
- Similarly, heat carriers move along the internal circuit of the custom micro-fluid channel plate It forms by a pack of plates.
- In the process of movement, in contact with the surface of the plate, the hotter coolant gives off part of the heat to the heated medium.
- From the outputs, the coolants, with a changed temperature, enter the heating, water supply or ventilation system.
- The inlet and outlet openings of heat exchangers can have a different cross-section (for Ridan units, the diameter reaches 500 mm)/. Similarly, with the help of branch pipes they are connected to the pipeline of the main system.
This principle of operation and the device of plate is quite easy to follow:
The principle of operation of the plate heat exchanger
Types of plate heat exchangers, depending on the design:
- collapsible;
- Furthermore, brazed;
- Moreover, welded;
- Semi-welded.
Gasketed plate heat exchangers
A gasketed custom micro-fluid channel plate is a device in which the main function of heat transfer between heat carriers performs by a plate pack. The media do not mix with each other due to the alternation of plates with dense rubber gaskets. Moreover, it forms two paths of movement.
This type of unit got its name "collapsible" because the plate pack does not assemble. Furthermore, it also disassembles during regular maintenance (flushing) or repair.
Structural diagram of a gasketed heat exchanger
The gasketed custom micro-fluid channel plate consists of the following elements:
- The fixed pressure plateis the main element.
- Theheat exchanger plates, come of stainless steel or titanium, press against each other using gaskets. Furthermore, the number of plates depends on technical parameters and equipment requirements.
- The plate packis the main functional element that forms the inner contour of the device and carries out heat exchange.
- Similarly, the supporting baseis a guide bar onto which the plates are put on during the assembly of the unit.
- Movable pressure plate- presses the entire package against the fixed pressure plate using fastening elements: tie bolts, bearings, lock washers.
- Support frame- The vertical element to which the guide beams (top and bottom beams) attach.
Due to the high speed of working media inside collapsible heat exchangers, deposits and blockages accumulate on its inner surfaces more slowly than on the surfaces of shell-and-tube units.
How does custom micro-fluid channel plate work?
The undoubted advantage of this type of maintenance is the possibility of complete disassembly of the apparatus. Furthermore, it allows not only washing the plates, but also their mechanical cleaning.
It is also worth noting that the possibility of complete disassembly of the unit makes it possible not to replace it entirely in cases of leaks, but to quickly identify non-working elements, change them and restart the heat exchanger in operation. If you have the necessary spare parts “at hand”, the whole procedure will take from several hours to 1 hour.
Brazed heat exchangers
Brazed heat exchangers also basically contain a package of plates, but the difference from collapsible heat exchangers is that they solder together. Furthermore, assembly / disassembly of such a package is impossible.
Soldering carries out using nickel or copper. Therefore, there are two main types of brazed plate heat exchangers: nickel brazed and copper brazed. Moreover, nickel solder is common for machines that will work with more aggressive environments.
Sectional view of the brazed plate heat exchanger
Brazed custom micro-fluid channel plate is mainly common in the household segment due to their low cost, simplicity and small size. Most often, this type of device is easy to find in heating systems of private houses. Here, a heat exchanger is connected to a water heating boiler.
Semi-welded heat exchangers
Semi-welded heat exchangers are units in which a package of plates is made in a combined way:
- plates weld together in pairs;
- Furthermore, seals are attached to the outside of such a double mini-bag;
- The next welded mini-bag attaches.
Places of pair welding of plates
This type of design allows the use of semi-welded heat exchangers in work with aggressive media or in cooling, since the welding of the plates excludes the possibility of freon leakage in the cooling circuit.
Welded heat exchangers
Welded heat exchangers are devices in which the plates are welded together without the use of seals.
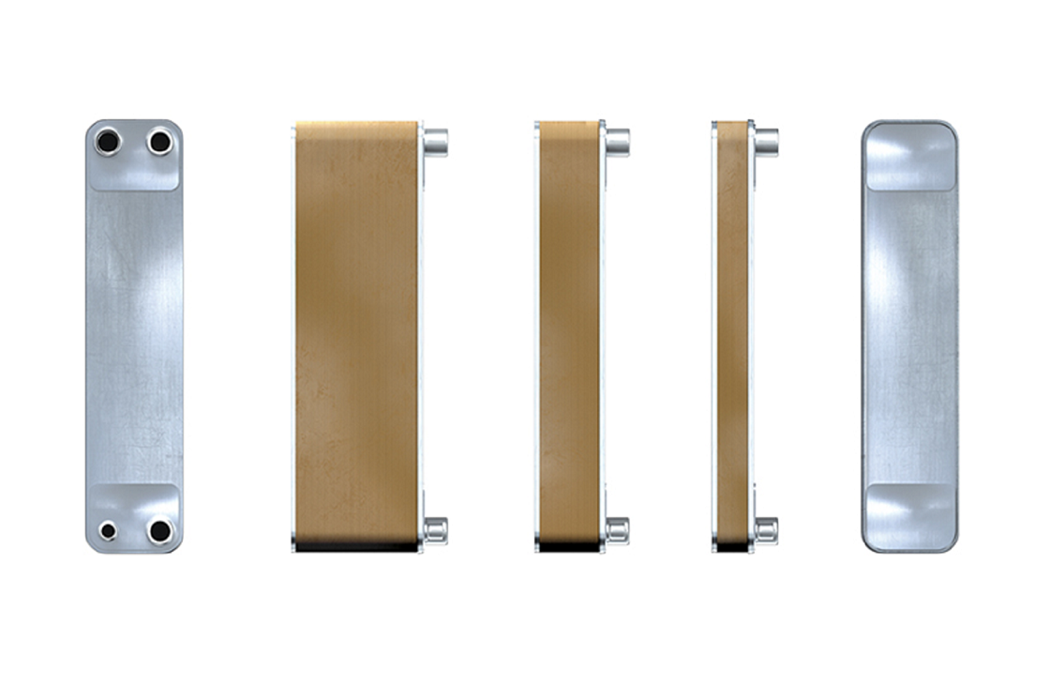

External view of the welded heat exchanger
One of the streams of coolants moves through corrugated channels, the second through tubular. Similarly, the principle of operation of a plate welded heat exchanger is easy to see:
The principle of operation of a welded custom micro-fluid channel plate
Welded heat exchangers are common in technical processes with extreme parameters: high temperatures (up to 900 degrees Celsius), pressure (up to 100 bar) and extremely aggressive media, since the absence of rubber seals and the welded method of adhesion exclude the possibility of leakage and mixing of media.
The main disadvantages of this type of units are: high cost and dimensions.
APPLICATION OF PLATE HEAT EXCHANGERS
Plate heat exchangers are common in:
- energy;
- heating;
- Furthermore, ventilation and air conditioning;
- shipping;
- Food Industry;
- Moreover, mechanical engineering;
- automotive industry;
- Similarly, metallurgy.
PROS AND CONS OF PLATE HEAT EXCHANGERS
Advantages:
- Convenience of transportation and installation, since the plate heat exchanger is smaller than other types of recuperative heat exchangers.
- Ease of maintenance- gasketed, semi-welded and welded heat exchangers are easy to flush, as they are either completely disassembled, as in the case of collapsible units, or partially, giving access to the plates, like semi-welded and welded devices.
- High productivity- the efficiency of plate aggregates reaches 95%.
- Price- the cost of custom micro-fluid channel plate is lower than similar shell-and-tube, spiral or block units.




